
It gives the disk - have at this point in the first case Point the same angular acceleration, which Replaced by a single mass point at the distance of 1 cm from the axis, you must - in order What is the meaning of these numbers? Answer: Set the disk into rotation byĪpplication of a force at 1 cm from its axis it will have aĬertain angular acceleration. we will omit the calculation - which is M This fact is expressed by the moment of inertia S mr 2 The first cases is quite a different body from that in the secondĬase. Regards the distribution of the mass about the axis, the disk in Second case many fewer points remain at rest. Rest, as has one diameter (2 r) of the disk, in the Points have the distance zero from the axis. , but in the case of the axis BB', all points on the Have the largest distance - we ignore the thickness of the disk! In the case of the axis AA', only two points (**) Largest distance which a point can have from the axis is rĬm. The disk is r cm, then, for example, in both cases the They are distributed differently aboutĮach of the axes AA' and BB'. The line through these points, you are also interested in which two points are to be held fixed - in other words, youĪlso want to know how its M kilograms are distributed around the axis. You want to keep two points of it fixed and rotate it about
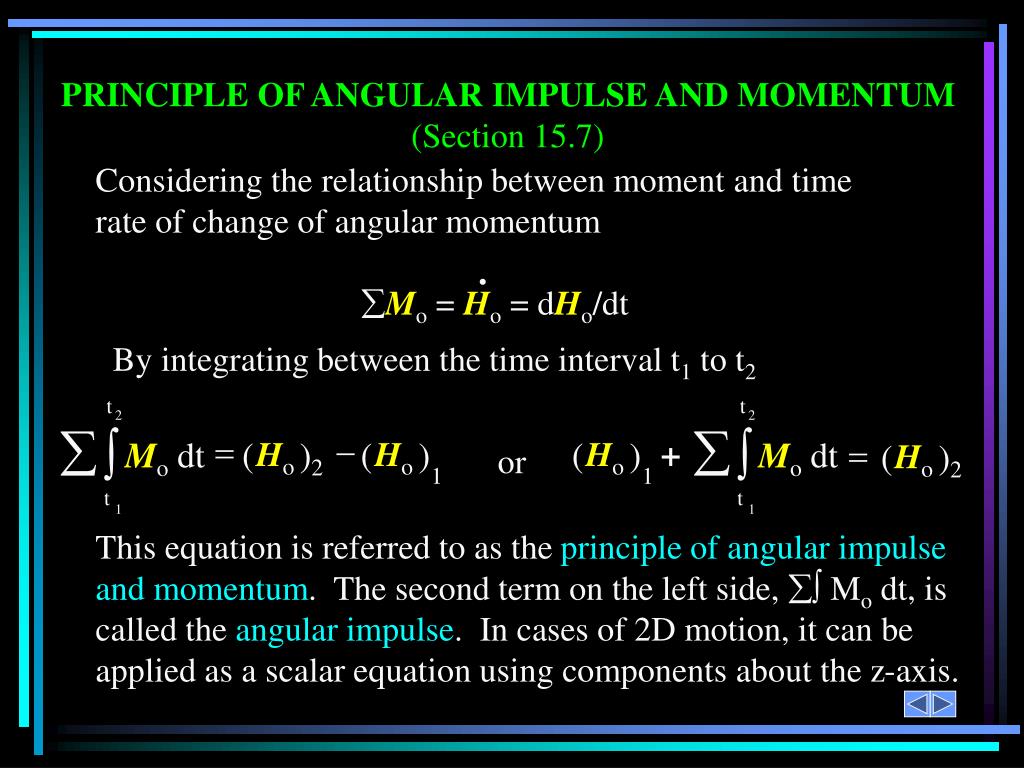
Interested in the number of kilograms it contains. Inertia of the body with respect to the instantaneous The sum over all mass points and always for that axis about which the body then rotates. 107, the sum only involves three mass points, in the case The same body with respect to different axes of rotation. Manifests the difference of the grouping of the mass points of The same mass points m move in both cases, but aboutĭifferent axes with the distances r and r. Relating to the axes A and A' side by side, you note that the difference between the two The end of unit time the angular velocity w, the forceġ cm from the axis A'A'. M 3 as it rotates about the axis A'A' will attain at M 3 is now to take place with the angular acceleration w about \(\Delta p\) = (2.0 kg)(-10 m/s) – (2.To each axis of rotation corresponds a moment of inertia. Now, calculate the impulse of the object. Moreover, after hitting the wall its velocity becomes -10 m/s (it is negative because it has bounced back in the opposite direction). Furthermore, before hitting the wall, the mass of the object is 2.0 kg and its velocity is 10 m/s.
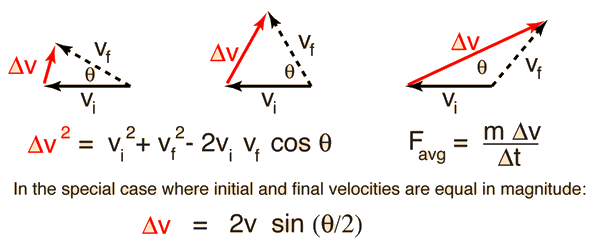
In this example, the object first collides with the wall and then bounce back. If the wright of the object was 2.0 kg and the object travels with a velocity of 10 m/s before it hit the wall.

Solved Example on Impulse Formula Example 1Īn object collides with a solid wall and after the collision, it stops. Also, impulse has two different units, it can either kilogram meter per second (kg m/s) or Newton times seconds (Ns). Most noteworthy, the formula relates impulse to the change in the momentum of the object. \(\vec\) = refers to the initial momentum

Besides, a slow-moving large object has large momentum also, a small but fast-moving object has a large momentum.Īs an example, suppose a Bowling ball and Ping-Pong ball have the same velocity, then the Bowling ball will have greater momentum because it is bigger than the Ping-Pong ball. Moreover, an object that is stable or stationary has no or zero momentum. Also, it is a measure of how difficult it is to stop an object. Momentum refers to the measure of strength. Hence, the question here is what is impulse and what it has to do with these situations?īefore discussing impulse we first need to converse about the concept of momentum. in all these things we use impulse without knowing it. In our daily life, we have kicked a ball, hit a punching bag, and played sports that involve any kind of ball, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
